1,Research Background
Immunologically cold tumors refer to those with insufficient immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment or the presence of immune cells with low activity, making it difficult to effectively recognize and attack tumor cells. Due to their weak immune response, these tumors typically exhibit poor responsiveness to immunotherapy.
In immunologically cold tumors, Gasdermin-mediated inflammatory cell death (pyroptosis) can activate protective immunity. This suggests that inducing pyroptosis in tumor cells may enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and attack tumor cells, thereby improving the efficacy of immunotherapy.
In this study, we explore why the NanoTemper molecular interaction platform provides critical data for cancer immunotherapy.
2,Research Content
Gasdermin is a class of proteins, and the development of GSDMD (Gasdermin D) agonists represents an emerging direction in current anti-tumor research, demonstrating significant therapeutic potential.
In September 2024, a team led by Hao Wu from Harvard Medical School published a research article titled "Small-molecule GSDMD Agonism in Tumors Stimulates Antitumor Immunity Without Toxicity" in Cell (Impact Factor: 45.5). Through high-throughput screening, the team identified a compound named DMB. This compound can directly activate GSDMD-mediated tumor cell perforation and pyroptosis without relying on traditional cleavage mechanisms, and it does so without causing significant toxicity. Additionally, DMB activates anti-tumor immune responses and prevents tumor recurrence.
The researchers utilized the Monolith Molecular Interaction Platform from NanoTemper Technologies in Germany to detect the binding of the small molecule DMB to GSDMD. The Monolith platform enabled the researchers to directly observe how the ligand activates GSDMD pore formation and pyroptosis without the need for GSDMD cleavage. This provided critical experimental data for the discovery and optimization of GSDMD agonists. This breakthrough offers a novel strategy for cancer immunotherapy.
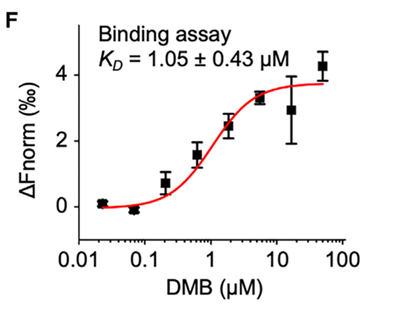
Figure: Monolith Molecular Interaction Platform for Detecting the Binding Between DMB and GSDMD
3,Technical Advantages
In this study, the Monolith Molecular Interaction Platform demonstrated its unique advantages during the assay process. It requires no prior processing of the protein, eliminating the need for the complex step of cleaving GSDMD. This approach directly maximizes the efficiency of molecular interaction detection, reduces sample consumption, and significantly simplifies experimental procedures. It is an essential detection tool for every researcher.

Molecular Interaction Analyzer
Effortless, Rapid, and Accurate Detection of Molecular Interactions
- Technical Modules: Spectral Shift and Temperature-Related Intensity Change (TRIC) / Microscale Thermophoresis (MST), with flexible upgrade options.
- No Sample Immobilization Required: Enables direct quantitative detection in solution.
- Molecular Weight Agnostic: Effortlessly handles various molecular interactions, including proteins, nucleic acids, peptides, small molecules, ions, nanoparticles, and more.
- Time and Sample Efficient: Detects one Kd in as little as 1.5 minutes, with a minimum sample consumption of only 4-10 μL.
- Intelligent Optimization: Real-time monitoring of sample quality and provision of optimization recommendations.
- No Liquid Flow System: Eliminates the risk of clogging and requires no maintenance.